Colour depth is describes the number of bits per pixel (bpp) that can be displayed on a computer. Each bit represents two colours, because it has a value of 0 or 1. The higher the colour depth, the more wider the range of distinct colours (more bpp = more colours displayed).
The following are examples of colour depth:
• 1-bit allows 2 colours
• 4-bit allows 4 colours
• 8-bit allows 256 colours
• 16-bit allows 65 536 colours
• 24-bit allows 16 777 216 colours
Showing posts with label graphic terms.. Show all posts
Showing posts with label graphic terms.. Show all posts
Friday, February 11, 2011
animated gif;
An animated GIF is one of many graphic file types. It is composed of several frames/layers of different images stacked on top of each other. These images, when compressed, can create a series of movement (animation). This file type is saved under the filename extension .gif.
The following are examples of animated GIFs:


framebuffer;
A framebuffer is an area of memory used to hold data/information for one frame or picture. This information consists of colour values fo every pixel on the screen. The framebuffer holds a bitmapped image as it is being displayed on the screen. It is the size of the maximum image that can be displayed on the screen.
compression;
Image compression is done by reducing the size of the original image/graphic file without degrading the quality to the point where the image is unrecognisable. This is done to save memory space and to lesson the time in which the file is sent/uploaded to the Internet. The most common method of image compression is by the saving the image in file formats such as JPEG and GIF.
filename extension;
A filename extension is a suffix added at the end of the name of a computer file. This is used to indicate the type of file and the file format (encoding convention). Some common filename extensions include: .jpg, .png, .gif, .psd, etc.
resolution;
The resolution of an image is the number of pixels per square inch/dots per inch (dpi) in a computer-generated image. It describes the details an image holds so the greater the resolution of an image, the better quality there is.
The following is a comparison between the same image, each with different resolutions:

The following is a comparison between the same image, each with different resolutions:

dpi;
Dots per inch;
DPI, very similar to PPI (pixels per inch), is the measure of the number of pixels per inch in an image/graphic. It is used to specify the image resolution and is a term to describe the measure of sharpness of an image.
DPI, very similar to PPI (pixels per inch), is the measure of the number of pixels per inch in an image/graphic. It is used to specify the image resolution and is a term to describe the measure of sharpness of an image.
cpu;
Central Processing Unit;
The CPU is a microchip that serves as the computer's 'brain' and 'heart'. It is this chip that receives data input, processes information and executes instructions.
The following is an image of the CPU (stored in -):
add image
The CPU is a microchip that serves as the computer's 'brain' and 'heart'. It is this chip that receives data input, processes information and executes instructions.
The following is an image of the CPU (stored in -):
add image
morph;
Morphing is a special effect to transform one image to another (or perhaps more). This transition from one image to the next is seamless, which means that the first image gradually changes features and characteristics until it completely matches the next.
The following is an example of morphing:

The following is an example of morphing:

frame;
A frame, in animation, is one layer of a still image. A compilation of frames together can form a series of movement (animation).
fps;
mirror;
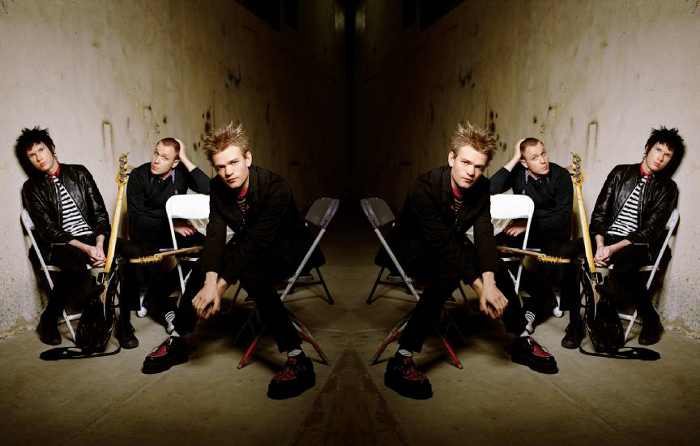
A method to adjust/alter an image is to mirror it. To mirror an image is the same as flipping - it is when an image is a reflected duplicate of the original image, only in reverse.
The following is an example of an image that is mirrored (horizontally):
The following is an example of an image that is mirrored (horizontally):
video card;
A video card is an expansion card that translates data from the CPU and display it on the monitor/screen. Also called graphics accelerators, video cards accelerates both 2D and 3D graphics rendering. Since almost all of the programs nowadays are graphics-oriented, the video card can make just about all programs run more efficiently.
flip;
Flipping is a method that can alter/adjust an image. By flipping, you create a reflection of the original image, somewhat like a mirror. An image can be flipped either horizontally or vertically. This is done by rotating the image 180 degrees.
The following is an image flipped vertically:


bmp
BMP is short for bitmap. The BMP format stores colour data for each pixel in the image without the use of compression. This makes the image appear sharper/crisper than other file formats that use compression and higher in quality. However, bitmap files are much larger in size, as opposed to other formats that compresses the image.
pixel;
A pixel is the smallest unit/element of an image that can be controlled. They are commonly depicted as dots or squares and each pixel can only be one colour. So an image is basically a compilation of individual dots (of different colours) on the screen. With art programs, we can specify the size of the canvas by using pixels.

The following is an example of an image magnified 2000%: (the pixels are more distinct)
jpeg;
Joint Photographic Experts Group;
JPEG is the standard file format for image compression. It is an image format that reduces the size of the original file. By saving in this format, the image gains a lossy compression - in which you lose the sharpness of the original image (blurrier). This file type can be saved under .jpg, .jpeg, .jfif, etc.

JPEG is the standard file format for image compression. It is an image format that reduces the size of the original file. By saving in this format, the image gains a lossy compression - in which you lose the sharpness of the original image (blurrier). This file type can be saved under .jpg, .jpeg, .jfif, etc.
The following is an example of an image saved in the .jpg file format:

Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)